steel profiles
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)
- Information
- Description
- Downloads
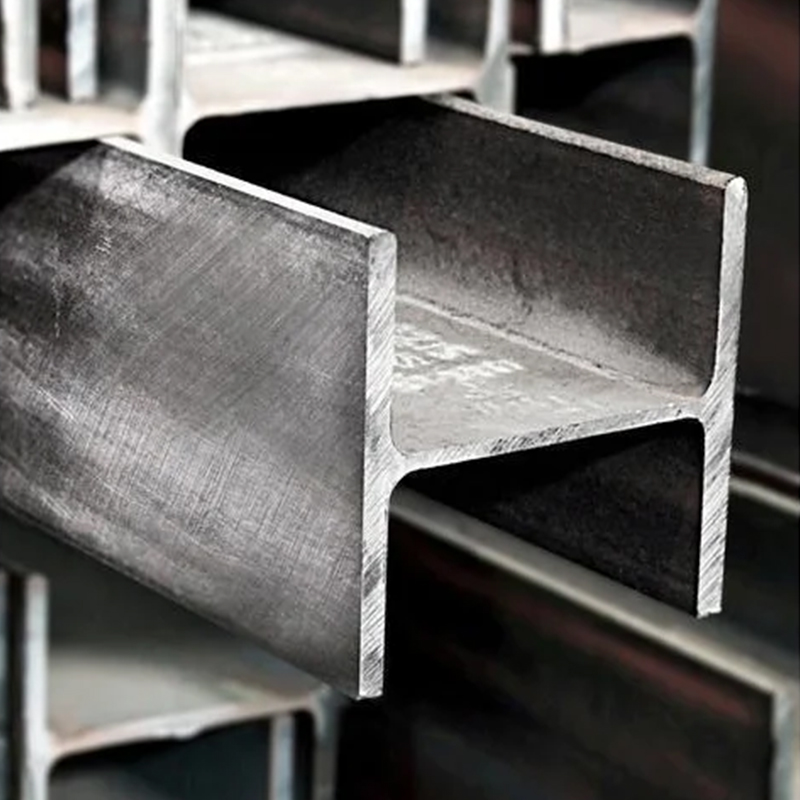
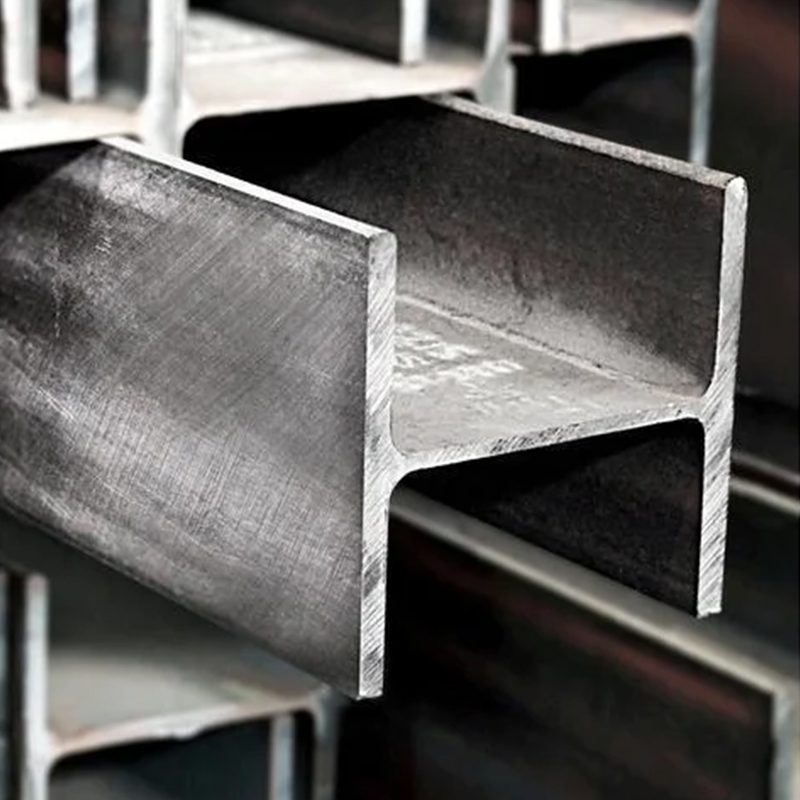
A profile is an object with a certain geometric shape made of iron or steel and materials with certain strength and toughness through processes such as rolling, extrusion, casting, etc. This type of material has a certain appearance size, a certain shape of the cross-section, and certain mechanical and physical properties.
Shapes can be used alone or further processed into other manufactured products, commonly used in building structures and manufacturing installations. Mechanical engineers can select specific shapes, materials, heat treatment states, mechanical properties, and other parameters of profiles according to design requirements, and then divide the profiles according to specific size and shape requirements, and further process or heat treat them to meet the accuracy requirements of the design. The material, specifications, and dimensions of profiles can refer to corresponding national standards.
The production of profiles has the following characteristics: (1) There are many varieties and specifications. There are over ten thousand types, and in production, with the exception of a few specialized rolling mills producing specialized products, the vast majority of profile rolling mills are producing multiple varieties and specifications. (2) There are significant differences in cross-sectional shapes.
There are five common classification methods for profiles: (1) Classified by production method, profiles can be divided into hot rolled profiles, cold formed profiles, cold rolled profiles, cold drawn profiles, extruded profiles, forged profiles, hot bent profiles, welded profiles, and special rolled profiles. (2) According to the characteristics of the cross-section, profiles can be classified into simple cross-section profiles and complex cross-section profiles based on their cross-sectional shape.
The cross-section of simple cross-section profiles is symmetrical, with a relatively uniform and simple appearance, such as round steel, wire rod, square steel, and arch steel.
Complex cross-section profiles, also known as irregular cross-section profiles, are characterized by distinct convex and concave branches in the cross-section. Therefore, it can be further divided into flange profiles, multi-step profiles, wide and thin profiles, local special processing profiles, irregular curve profiles, composite profiles, periodic cross-section profiles, and metal wire profiles, etc. (3) Classification of profiles by user department: Railway profiles (steel rails, fishplates, turnout rails, wheels, tires), automotive profiles (rims, tire retainers, and lock rings), shipbuilding profiles (L-shaped steel, ball flat steel, Z-shaped steel, ship window frame steel), structural and architectural profiles (H-shaped steel, I-shaped steel, channel steel, angle steel, crane rails, window and door frame materials, steel sheet piles, etc.) Mining steel (U-shaped steel, groove steel, mining I-shaped steel, scraper steel, etc.), mechanical manufacturing profiles, etc. (4) Classified by cross-sectional size, profiles can be divided into large, medium, and small profiles based on their respective suitability for rolling on large, medium, and small rolling mills. The distinction between large, medium, and small is actually not strict.
In addition, there is a method of distinguishing by unit weight (kg/m). It is generally believed that small profiles have a unit weight of less than 5 kg/m, medium profiles have a unit weight of 5-20 kg/m, and large profiles have a unit weight exceeding 20 kg/m.
Shapes can be used alone or further processed into other manufactured products, commonly used in building structures and manufacturing installations. Mechanical engineers can select specific shapes, materials, heat treatment states, mechanical properties, and other parameters of profiles according to design requirements, and then divide the profiles according to specific size and shape requirements, and further process or heat treat them to meet the accuracy requirements of the design. The material, specifications, and dimensions of profiles can refer to corresponding national standards.
The production of profiles has the following characteristics: (1) There are many varieties and specifications. There are over ten thousand types, and in production, with the exception of a few specialized rolling mills producing specialized products, the vast majority of profile rolling mills are producing multiple varieties and specifications. (2) There are significant differences in cross-sectional shapes.
There are five common classification methods for profiles: (1) Classified by production method, profiles can be divided into hot rolled profiles, cold formed profiles, cold rolled profiles, cold drawn profiles, extruded profiles, forged profiles, hot bent profiles, welded profiles, and special rolled profiles. (2) According to the characteristics of the cross-section, profiles can be classified into simple cross-section profiles and complex cross-section profiles based on their cross-sectional shape.
The cross-section of simple cross-section profiles is symmetrical, with a relatively uniform and simple appearance, such as round steel, wire rod, square steel, and arch steel.
Complex cross-section profiles, also known as irregular cross-section profiles, are characterized by distinct convex and concave branches in the cross-section. Therefore, it can be further divided into flange profiles, multi-step profiles, wide and thin profiles, local special processing profiles, irregular curve profiles, composite profiles, periodic cross-section profiles, and metal wire profiles, etc. (3) Classification of profiles by user department: Railway profiles (steel rails, fishplates, turnout rails, wheels, tires), automotive profiles (rims, tire retainers, and lock rings), shipbuilding profiles (L-shaped steel, ball flat steel, Z-shaped steel, ship window frame steel), structural and architectural profiles (H-shaped steel, I-shaped steel, channel steel, angle steel, crane rails, window and door frame materials, steel sheet piles, etc.) Mining steel (U-shaped steel, groove steel, mining I-shaped steel, scraper steel, etc.), mechanical manufacturing profiles, etc. (4) Classified by cross-sectional size, profiles can be divided into large, medium, and small profiles based on their respective suitability for rolling on large, medium, and small rolling mills. The distinction between large, medium, and small is actually not strict.
In addition, there is a method of distinguishing by unit weight (kg/m). It is generally believed that small profiles have a unit weight of less than 5 kg/m, medium profiles have a unit weight of 5-20 kg/m, and large profiles have a unit weight exceeding 20 kg/m.