- Home
- >
- Product
- >
- steel Coil
- >
- sheet steel
- >
- View Details
sheet steel
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)
- Information
- Description
- Downloads
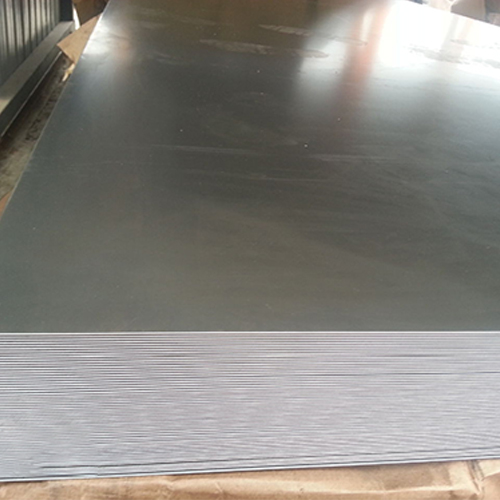
Thin steel plate is a steel plate with a thickness between 0.2 and 4mm produced by hot rolling or cold rolling methods.
The width of the thin steel plate is between 500 and 2500mm. According to different purposes, thin steel plates have different materials: ordinary carbon steel, high-quality carbon structural steel, alloy structural steel, carbon tool steel, stainless steel, spring steel, electrical silicon steel, and so on. They are mainly used in sectors such as the automotive industry, aviation industry, enamel industry, electrical industry, and mechanical industry. Thin steel plates can be delivered directly after rolling, as well as those that have been pickled (pickled thin steel plates), galvanized or tinned.
Strip steel is actually a very long thin plate, supplied in coils. Strip steel can be produced on a multi stand continuous rolling mill, and cut into a fixed length to form a steel plate. Therefore, the productivity is higher than that of single sheet rolling.
Purpose: Blanking
Blanking is a stamping process that uses a die to separate materials. Blanking, broadly speaking, is the general term for the separation process, which includes various processes such as cutting, blanking, punching, trimming, and cutting. But generally speaking, the punching process mainly refers to the process of cutting and punching out finished parts, and can also be used to prepare blanks for other forming processes.
After punching, the sheet metal is divided into two parts, namely the material falling part and the material carrying part L. If the purpose of punching is to produce a certain shape of the recoil part, then this punching process is called blanking; If it is to make an inner hole, it is called punching.
According to different deformation mechanisms, punching can be divided into two categories: ordinary punching and precision punching.
The width of the thin steel plate is between 500 and 2500mm. According to different purposes, thin steel plates have different materials: ordinary carbon steel, high-quality carbon structural steel, alloy structural steel, carbon tool steel, stainless steel, spring steel, electrical silicon steel, and so on. They are mainly used in sectors such as the automotive industry, aviation industry, enamel industry, electrical industry, and mechanical industry. Thin steel plates can be delivered directly after rolling, as well as those that have been pickled (pickled thin steel plates), galvanized or tinned.
Strip steel is actually a very long thin plate, supplied in coils. Strip steel can be produced on a multi stand continuous rolling mill, and cut into a fixed length to form a steel plate. Therefore, the productivity is higher than that of single sheet rolling.
Purpose: Blanking
Blanking is a stamping process that uses a die to separate materials. Blanking, broadly speaking, is the general term for the separation process, which includes various processes such as cutting, blanking, punching, trimming, and cutting. But generally speaking, the punching process mainly refers to the process of cutting and punching out finished parts, and can also be used to prepare blanks for other forming processes.
After punching, the sheet metal is divided into two parts, namely the material falling part and the material carrying part L. If the purpose of punching is to produce a certain shape of the recoil part, then this punching process is called blanking; If it is to make an inner hole, it is called punching.
According to different deformation mechanisms, punching can be divided into two categories: ordinary punching and precision punching.